
It also includes planning related to the production of energy and its storage for future usage. To make things simple, we can define Energy management as a process that involves optimization of energy use for the best possible outcomes and taking steps for its conservation. What is Energy Management?Īs per Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI), which is an organization with 150,000+ engineers and scientists, energy management is defined as follows-Įnergy management is the proactive, organized, and systematic coordination of procurement, conversion, distribution, and use of energy to meet the requirements, taking into account environmental and economic objectives. And finally, we’ll also introduce to you our Energy Monitoring System and what else we do. So, this will be an in-all-one article for you on energy management. So in this article, we are going to give you more details on the process of energy management covering all the aspects that we just mentioned above, will give to essential reasons for energy management and will also describe what an energy management system does. The process also has a role to play in many areas like Logistics, Industrial Production, Machine Maintenance, the Energy Procurement Process itself, and even your Personal Life. But here’s the fact – energy management covers more than just switching on & off lights & fans. Now, the term – energy management – might be bringing to you an image of just switching off some unused lights and appliances. So, efficient energy usage is the solution for this world’s ever-rising energy hunger. As per the data available, the total energy consumption of the world is expected to increase by 48% before 2040, says a report published by US Energy Information Administration(EIA).īut favorably, employing an energy management system(EMS) in a building – that aims to make use of the energy sources efficiently – may save up to 29% on energy consumption costs.

The efficiency of the nation’s cars, lightbulbs and factories determines how much waste heat is produced and how much fuel and electricity can be put to productive use.Our world is already fraught with rising energy demands. This energy most often takes the form of waste heat, such as the warm exhaust from automobiles and furnaces. Although data are not yet available on specific uses within the sector, "it is likely the result of increased manufacturing, petrochemical production and refining of fuel for export," Simon said.Īll energy use results in some losses, shown on the charts as rejected energy. Petroleum use (oil) was up 0.7 quads or 2 percent, but barely budged in the dominant transportation sector. However, it rose substantially in the industrial sector. Biofuel use in transportation, which is dominated by ethanol use in gasoline, was essentially unchanged since 2017. Most of the increase in biomass use was in the residential sector for heating. It also had a colder winter, which increased gas demand in the residential sector."Ĭoal consumption continued to fall in 2018 by 0.7 quads or 5 percent, due mainly to increases in natural gas and renewable use.īiomass use was up by about 0.2 quads or 5 percent from 2017 levels. "2018 had a hotter summer than 2017, requiring more electricity for air conditioning, driving up gas consumption. "This reflects a significant increase to electricity generation, where gas continues to displace coal," Simon said. Supply from natural gas increased by 3 quadrillion BTU, from 28 in 2017 to 31 in 2018, a 10.7 percent increase. Wind and solar combined now produce more electricity than hydroelectric power, which dominated renewable energy for decades.
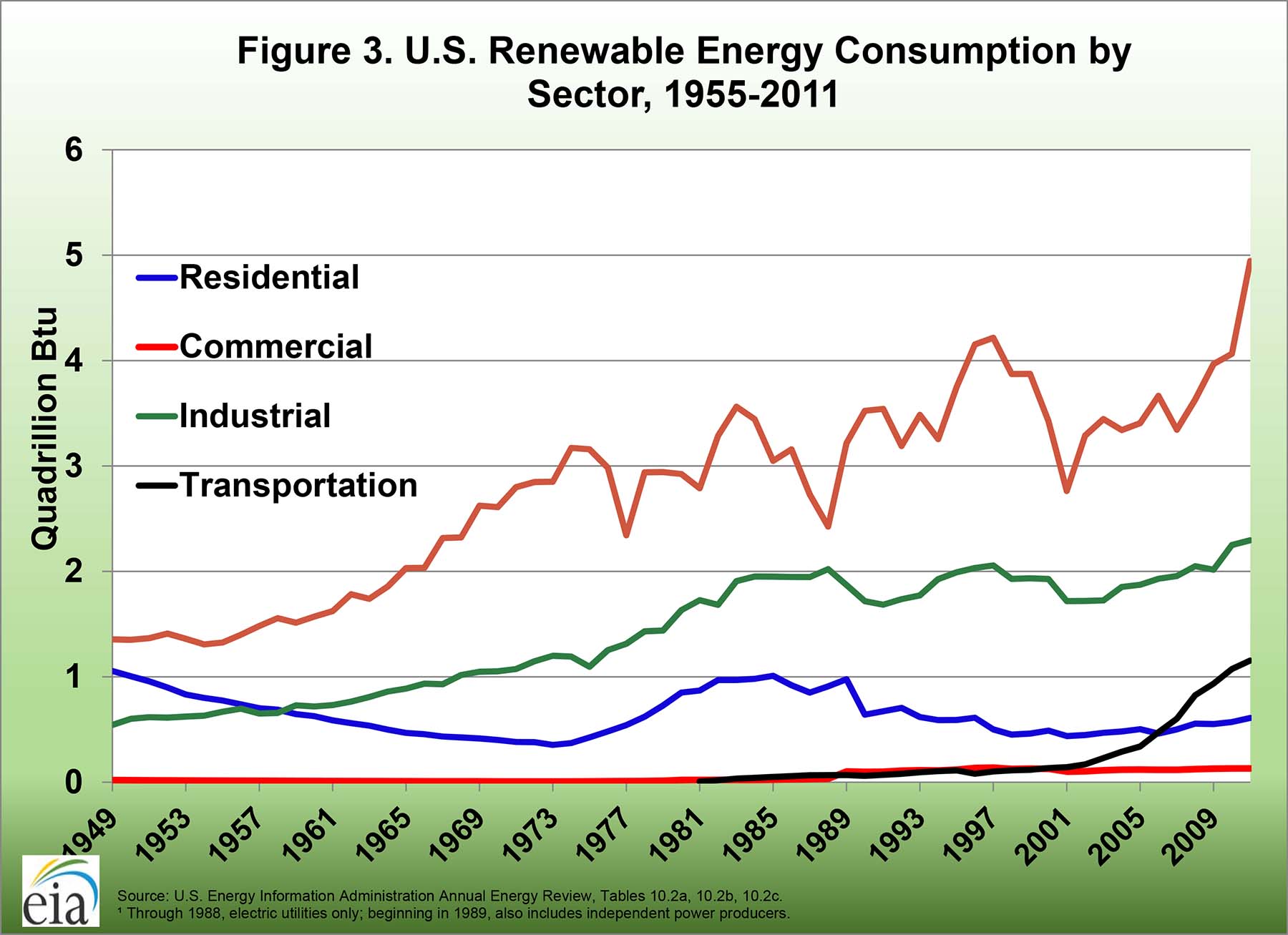
Over the last decade (between 20), total renewable energy production has doubled, including a five-fold increase in wind power and a 48-fold increase in solar. In 2018, wind use was up 0.18 quads (7.6 percent) and solar was up 0.18 quads (22 percent). The largest increases in energy supply came from natural gas, wind and solar energy. A BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a unit of measurement for energy 3,400 BTUs is equivalent to about 1 kilowatt-hour. Americans used 3.5 quads (quadrillion BTU) more in 2018 than in 2017. Energy use went up by 3.6 percent from 2017, which also is the largest annual increase since 2010.Įach year, the Laboratory releases energy flow charts that illustrate the nation's consumption and use of energy. The prior record, set in 2007, was 101.0 quads. Overall total energy consumption rose to 101.2 quadrillion BTU (or "quads"). Americans used more energy in 2018 than in any other year, according to the most recent energy flow charts released by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory ( LLNL).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
